What you need to know about your thyroid.
What you need to know about your thyroid — it controls a lot more than you think.
Your thyroid can have a big impact on your body. It can affect your weight, body temperature, mood, and more. Millions of Americans have thyroid conditions and many are not aware and go untreated.
The thyroid has always seemed to have an element of mystery to it. What exactly does it do? Where is it? And how can you make sure it’s healthy?
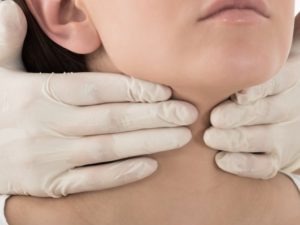
Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland which sits in your neck.
The thyroid sits low in the front of your neck with two wings on either side of the windpipe. It’s reddish-brown in color from its rich blood supply, said Matthew Hoffman, MD for WebMD.
You can’t feel a normal-sized thyroid.
The average thyroid is about two inches wide. When your thyroid is healthy you should not be able to feel it. Certain conditions can cause the thyroid to swell or to form nodules, which a doctor may be able to see or feel through the skin.
Your thyroid accomplishes its work through hormones.
The thyroid produces three hormones: triiodothyronine (T3), tetraiodothyronine (T4, or thyroxine), and calcitonin. T3 and T4 accomplish most of the functions directed by the thyroid, while calcitonin affects calcium and bone metabolism.
The pituitary gland controls the thyroid.
The pituitary, a peanut-sized gland known for its role in puberty, regulates the thyroid. The pituitary gland ‘tells’ the thyroid gland whether to release more or less hormones into the bloodstream, through the aptly-termed “thyroid-stimulating hormone” (TSH).
Abnormal levels of TSH may indicate that your thyroid is producing too much or too little thyroid hormone. TSH testing is the easiest and most accurate way to see if your thyroid is working irregularly.
Your thyroid affects a lot more than your energy level. It plays an important role in almost every major system of the human body. Virtually every tissue in the body is affected or regulated by thyroid hormone.
Thyroid hormones control the speed at which the body’s chemical functions proceed and also stimulate cells to produce certain proteins or increase the amount of oxygen they use.
Thyroid hormones affect many vital body functions, such as the heart rate, the rate at which calories are burned, skin maintenance, growth, heat production, fertility, and digestion.
Body Temperature
Your body temperature is increased when more thyroid hormones are produced. That’s why people with thyroid disorders may feel hotter or colder than others.
Your thyroid stores extremely concentrated amounts of hormones.
The thyroid can store large amounts of hormone— extreme amounts would certainly not be a good thing. The good news is that the thyroid hormone is very tightly regulated by constant, sensitive signals traveling between the brain, the gland, the body’s tissues, and the blood concentrations of the hormone at any given moment.
Over 12 million Americans have a thyroid condition, according to the American Thyroid Association.
More than 12% of the US population will develop a thyroid condition in their lifetime, with up to 60% of those people being unaware of their condition. The American Thyroid Association website also states that most causes of thyroid conditions are unknown and that women are at higher risk for such conditions. But, these conditions can also be managed with the help of the doctor.
Here is a list of some of the major thyroid conditions:
- Hypothyroidism: low thyroid hormone production (autoimmune disease such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) is the common cause
- Hyperthyroidism: high thyroid hormone production (Grave’s disease is a common cause)
- Thyroid cancer: an uncommon form of cancer that is usually curable.
Sudden fatigue and weight gain could be signs of an underactive thyroid.
Depression, constipation, sensitivity to cold, and reduced sweating are also symptoms of hypothyroidism. These symptoms have multiple potential causes so it’s always best to check with your doctor who may decide to check the thyroid hormone and TSH levels.
A pounding heart, excessive sweating, and insomnia might signal an overactive thyroid.
Other signs of hyperthyroidism include diarrhea, nervousness, trembling, and sensitivity to heat. Again, check with your doctor – approx. 1 in 100 people have an overactive thyroid.
Can medications affect your thyroid function?
Certain medications can increase or decrease thyroid function or the amount of thyroid hormone in the body. Some of these include Amiodarone, Glucocorticoid, Iodide, Lithium, and Phenytoin.